
手写数字识别是一个典型的分类问题,目标是将输入的28x28像素的手写数字图片分类为0~9中的一个数字。通过机器学习模型(如Softmax回归)对图片进行特征提取和分类,最终输出概率最大的数字作为识别结果。
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('input_data/', one_hot=True)
MNIST数据集包含55000张训练图片、10000张测试图片和5000张验证图片。每张图片被转换为784维的一维数组。
使用Softmax回归模型:
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # 输入图片
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10])) # 权重矩阵
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) # 偏置项
y = tf.matmul(x, W) + b # 模型输出
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) # 真实标签
使用交叉熵作为损失函数,并通过梯度下降法优化模型:
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_, logits=y))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
for _ in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) # 随机选取100个样本
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
print(sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels}))
模型在测试集上的准确率可达约92%。
金鸣表格文字识别程序提供了专门的手写识别和数字识别功能,适用于实际应用场景中的手写数字识别需求。
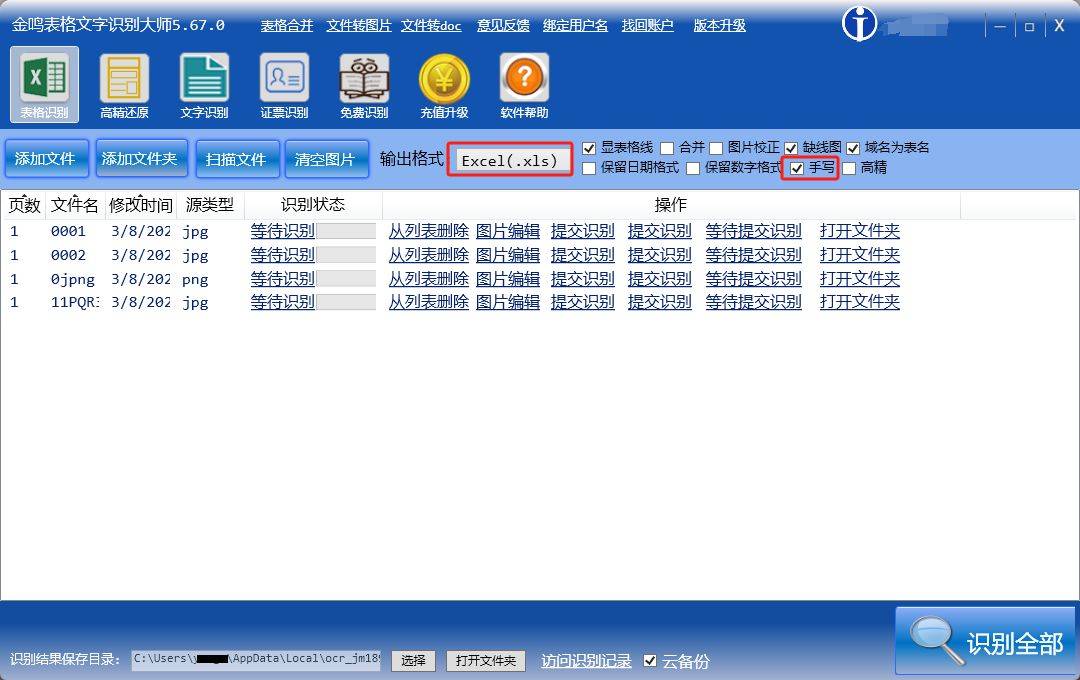
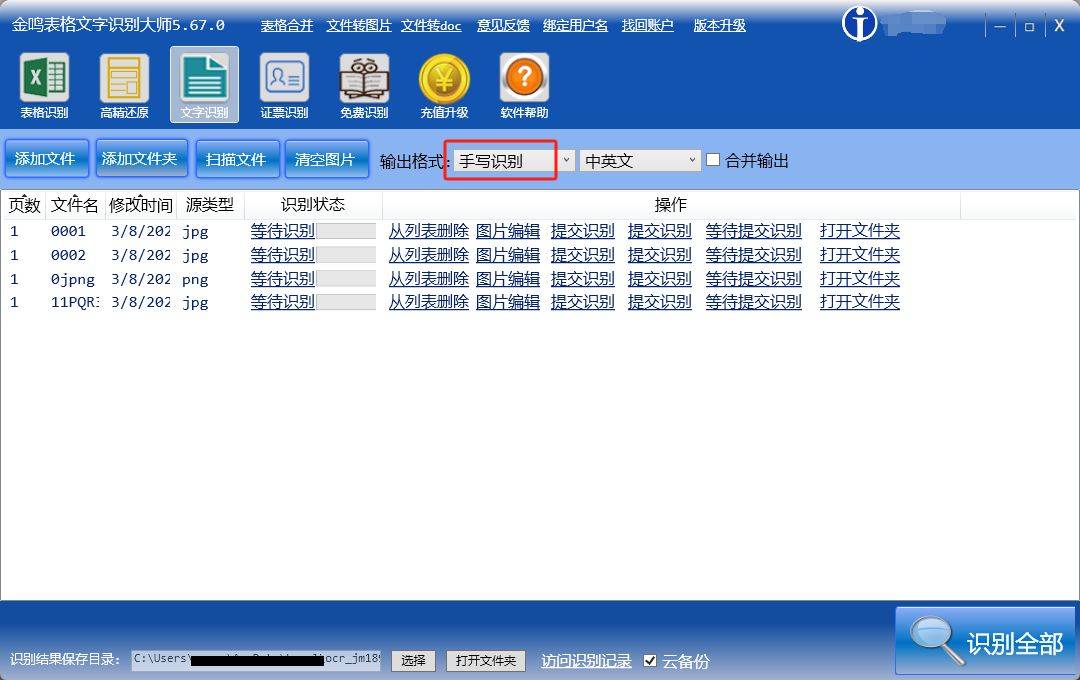
根据实际需求选择合适的解决方案,可以高效地完成手写数字OCR文字识别任务。